- All
- Mutual Funds
- Corporate Fixed Deposits
- Equity Trading
- Health Insurance
- Motor Insurance
- Travel Insurance
- Life Insurance
What are the benefits of a regular health insurance plan?
A medical contingency is becoming very frequent due to our changing lifestyles. Any such contingency when occurs results in a huge financial loss. A health insurance plan provides insurance coverage against such financial loss. The plan pays the medical expenses which occur in case of any emergency or medical treatment. Thus, the plan protects our savings against the impact of medical expenses which are high. Through a health insurance plan, one can get coverage for medical expenses incurred before and after hospitalization, hospitalization expenses, ambulance expenses, organ donor expenses, day care treatments and even maternity related expenses.
How much health insurance coverage should I have?
Medical treatments and procedures have improved. Such an improvement has also raised the resultant cost of such treatments. As such, medical inflation is high and is expected to increase in the future too. Coupled with such rising expenses, the incidence of diseases and accidents has also increased. More and more people are developing common lifestyle related ailments or are falling prey to accidents. In such a scenario, the hospital bills have the potential to run into lakhs. As such, the cover for a health plan should be sufficient to meet such high costs. Thus, while selecting the cover, we should bear in mind the expected cost of treatment, inflation and also the affordability of the premium. After considering these factors, a sufficient coverage level should be selected so that the family is protected from the unforeseen medical exigencies of its members. Click here to check your optimum health insurance coverage.
When should a health insurance plan be taken?
A health insurance plan should be taken at the earliest. At a young age, a health plan can be availed easily at lower premiums. Moreover, since the chance of having any ailment at a lower age is negligible, an all-inclusive coverage can be availed. After buying the plan when you wouldn’t be making any claim, you could also earn cumulative bonuses which would increase the coverage level without increasing the premium. Thus, buying early is advantageous and one should buy a health plan at the earliest. Thus, if you have not taken a health insurance plan yet and is eligible to opt for one, it is always prudent to apply for the same ASAP without much thought.
Who needs a health insurance plan?
Everyone needs a health insurance plan. Diseases and accidents can befall anyone. In that case, one would have to seek medical assistance and bear the huge costs. By having a health insurance plan, such costs can be compensated. Your finances would be insured against any medical costs. Thus, a health plan is a universal requirement and should be taken by everyone.
I have company provided health insurance. Why should I take an individual one?
Despite being covered under a group health plan, an individual health plan is always recommended. Group health plans have a limited coverage while individual plans provide a more exhaustive coverage. Group health plans usually continue only till the individual is employed with the company. On leaving the company, the company sponsored health plan stops and thus you may end up losing all continuity benefits that had been accrued over the years. Moreover, the level of group health cover is usually insufficient in covering a medical emergency. Individual plans bridge such coverage gaps, are customizable, have a wide scope of coverage and also continue lifelong. Also, individual health plans provide an additional tax advantage which cannot be availed in case of group health plans.
How do I choose which is the best health insurance plan for myself and my family?
There are a lot of health insurance plans available in the market today. As such, choosing the best one requires some simple research and comparison. While comparing health insurance plans, one must look at the medical expenses which the plan covers, the limit (if any) on such expenses, the claim settlement record of the company which is offering the plan, the premium charged, the waiting period for existing diseases, bonus and discounts which the plan offers. The best plan is ideally the one which has an exhaustive coverage, has minimal or no limits on the medical expenses which are covered, provide good discounts and bonuses and the premium rate of such plan is also reasonable.
What is it that I need to consider when buying a health insurance plan?
When buying any health insurance plan, attention must be given to the coverage features. Coverage features include the medical expenses which the plan undertakes to cover and any limits on such expenses if specified. Along with the coverage, the corresponding premium must also be checked to ascertain whether the premium rate is justified against the coverage provided. Other things which should be considered are the company’s claim settlement history, special discounts or features and the listed exclusions. It is always advisable to compare between the available health plans before finalizing one plan.
What does a health insurance cover?
A health insurance plan provides insurance against medical expenses which are incurred upon hospitalization. Among the expenses covered, some common coverage features that almost all health plans provide include pre-hospitalization, actual hospitalization which also includes rom rent, surgery cost, doctor’s fees, nurse’s fee, etc., post-hospitalization, organ donor expenses, day care procedures and ambulance expenses. Some plans also provide additional coverage features like maternity cover, cover for AYUSH treatments, out-patient expenses, etc.
What are the tax exemptions of a health insurance plan?
Premiums which are paid for a health insurance plan are exempted from taxation under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act. However, there is a limit to this exemption which is explained below:
| Instances | Exempted limit for coverage of self, spouse and dependent children | Exempted limit for coverage of parents | Total available deductible limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| None of the members are above 60 years of age | Up to Rs.25,000 | Up to Rs.25,000 | Up to Rs.50,000 |
| Only parents are above 60 years of age | Up to Rs.25,000 | Up to Rs.30,000 | Up to Rs.55,000 |
| The eldest member among self, spouse and children is above 60years of age and parents are also above 60 years of age. | Up to Rs.30,000 | Up to Rs.30,000 | Up to Rs.60,000 |
What do you mean by pre-existing disease or conditions?
A health insurance plan covers the medical expenses of such diseases or conditions which occur after the policy has been purchased. At the time of buying the policy if the policyholder or any of his family members who are being covered suffer from any ailment or any disease, such diseases or ailments are not covered in the initial few years of the plan. This period when the existing ailments are excluded from coverage is called the waiting period and the ailments or conditions are called pre-existing illnesses.
can I indemnify or claim benefits under the policy?
The policy benefits are payable only when you are hospitalization. On hospitalization, you have to inform the insurer. A pre-authorization form is required to be filled in and submitted for facilitating cashless claim settlement. If the hospitalization is a planned hospitalization, this form should be submitted 2-4 days in advance. In case of an emergency hospitalization, the form should be submitted within 24 hours. The insurer would then settle the medical expenses directly with the hospital. You would then have to submit all the medical bills to the insurance company along with other documents which may be demanded by the company.
I am a foreign citizen. Can I take a health plan for my child who is continuing further studies in India?
Yes, a foreign citizen can buy a health plan for his child who is studying in India. However, the coverage of the plan would be against the medical expenses which are incurred on treatments taken in India only.
Does premium increase every year?
The premium for a health insurance policy primarily depends on the age of the insured member. Insurance companies usually maintain age brackets and the premium rate for individuals in the same age bracket is same. So, when you renew the policy next year, if you are within the same age bracket, the premium would not increase. However, if the age bracket changes in any year, the resultant premium would increase.
Should I declare about my hospitalization and other illnesses or be quiet about it?
Insurance policies are subject to the principle of Utmost Good Faith. Under this principle, it is mandatory to disclose all your medical history correctly and truly to the insurance company. If you be quiet about it, the insurer would have the authority to reject your claim if it is found that you hid your medical history from the company. So, to ensure a fair claim settlement, you should always disclose about any hospitalization or other illnesses that you suffer from.
What is a senior citizen plan?
There are many health plans available in the market today which are designed especially for the senior citizens. Individuals aged above 60 years of age are the targeted customers of the plan. These plans are called senior citizen plans. The coverage features of these plans are customized to suit the requirement of older individuals. The waiting period for pre-existing illnesses is very low as older people have such illnesses. The coverage is also less restrictive in nature.
How does a senior citizen plan work?
Individuals aged 60 years and above can buy senior citizen health plans where other health plans might not be available for them. The plan can be bought easily with relaxed underwriting norms. However, the person to be covered might be required to undergo a health check-up before the policy is issued. The premiums are usually higher considering the age of the insured. There is a co- pay clause in the policy. This clause mandates the policyholder to bear a pre-defined proportion of the claim out of his pocket while the company would settle the remaining amount. Senior citizen health plans once taken are usually renewable for life.
What is the additional benefit of taking a senior citizen health plan over a normal health plan?
Senior citizen health plans are ideal for covering parents separately. If included in a family floater plan, the premium shoots up irrationally. Thus, a separate senior citizen health plan is good for covering parents separately. These plans have lower waiting periods and so any existing ailments of older individuals would be covered after a shorter duration compared to a normal health plan. even the coverage of a senior citizen plan would be more inclusive than a normal health plan.
How long can/should I continue my senior citizen plan?
The senior citizen plan should be continued throughout your lifetime. Thanks to the current IRDA regulation, most senior citizen plans are renewable for the entire lifetime and should be continued without a break.
I have a family history of diabetes. Should I opt for diabetic special health plans?
If you are not suffering from diabetes currently, you can opt for a normal health plan where you would get coverage for diabetes related ailments after the waiting period. This would make sense if you contract diabetes in future. However, if the company adopts a strict conditions on the chances of covering your diabetes in future or if excludes the coverage since the probability of diabetes is high, a diabetic special health plan would be more useful. The plan would cover your diabetes whenever you get it without strict rules or exclusions.
What are the benefits of diabetes special health plans over normal health plans?
Where normal health plans categorize diabetes as a pre-existing illness and have a long waiting period for its coverage, diabetes special plans cover diabetes after a very short or no waiting period. These plans cover most of the complications which diabetes might cause which may be otherwise excluded from the coverage of a normal health plan. Moreover, if under a normal health plan the company finds the diabetes to be severe, the coverage might be excluded altogether or included with many restrictions. This hurdle is overcome with a diabetes special health plan.
What is a critical illness plan?
A critical illness plan is a specialized health insurance plan. The plan covers a list of pre-defined critical illnesses. When the insured is diagnosed with any of the covered illnesses, a lump sum amount of money is paid by the insurance company. This amount is the Sum Assured chosen under the plan. Since a lump sum benefit is paid irrespective of the actual costs of treatment, these plans are also called fixed benefit plans. The lump sum amount received can be used by the policyholder in any which way necessary.
What are the critical illnesses these plans cover?
The list of critical illnesses covered by critical illness plans differ from plan to plan. However, some of the common critical illnesses which are covered by a critical illness plan include first heart attack of specified severity, cancer of specified severity, stroke resulting in permanent symptoms, repair of heart valves or open heart replacement, open chest CABG, coma of specified severity, aplastic anemia, major organ or bone marrow transplant, kidney failure resulting in dialysis, multiple sclerosis with persisting symptoms, bacterial meningitis, paralysis of limbs which is permanent in nature, etc.
Why should I take a critical illness plan?
Critical illness plans can be used to supplement your existing health plans. The cost of treatment of critical illnesses is huge and might not be covered completely by a regular health plan. These plans, by nature, provide a lump sum benefit for meeting such high expenses. A critical illness plan pays a lump sum amount irrespective of the actual expenses incurred. This amount can be used to meet the lifestyle expenses and the recovery expenses incurred due to a critical illness. Lastly, critical illnesses are becoming increasingly common and their financial implications require a sound coverage. Thus, critical illness plans are beneficial for you and your finances.
What is the difference between a critical illness plan and a regular health plan?
The difference between a critical illness plan and a regular health plan is highlighted in the table below:
| Points of difference | Regular health plans | Critical illness plans |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Indemnity plans | Fixed benefits plans |
| Coverage | A regular health plan provides an exhaustive coverage in terms of pre and post hospitalization, in-patient hospitalization, ambulance costs, organ donor expenses, day care treatments, etc. | A critical illness plan covers only a pre-specified list of critical illnesses. This list of illnesses varies from plan to plan. |
| Benefits | These plans pay the actual medical bills incurred on the covered expenses subject to the limit of the Sum Assured. | These plans pay the entire Sum Assured irrespective of the actual expenses incurred on diagnosis of the covered illness. |
What is a family floater plan?
A family floater plan is a health insurance plan which covers the entire family under a single policy. There is one Sum Assured and every family member shares the Sum Assured individually and jointly. On hospitalization, any member who is insured under the plan can avail coverage up to the entire Sum Assured.
Which is a better option – individual health plan or family floater plan?
A family floater health insurance plan is better because it covers the entire family members under a single plan and enables a higher level of Sum Assured to be shared among the embers. Moreover, a family floater health plan comes cheaper compared to an individual health plan for all family members.
What is the basic difference between individual and group health insurance coverage?
While an individual health plan is a voluntary choice, you would be covered under a group health plan by virtue of being a part of the group which has a plan for its members. The Sum Assured under a group health plan would be determined by the insurance company and would be limited whereas you can select your own level of coverage in an individual plan. Premiums for the group cover can be paid by you or by the group head entirely or partly as per the agreed terms while you have to pay your premium yourself in an individual health plan. Coverage extended under a group health plan is also limited as compared to a regular health plan. Lastly, individual health plans are renewable for lifetime while a group plan continues as long as you are associated with the group.
What is a cashless claim?
A cashless claim is one where you wouldn’t have to bear any medical expenses. The hospital would send the bills directly to the insurer and the claim would be settled. For availing a cashless claim settlement facility, you should avail treatment in a network hospital which is tied-up with the insurer to provide cashless treatment.
What is the procedure for availing the cashless benefit?
First and foremost, one should seek hospitalization in a network hospital for availing the cashless benefit. After that, a pre-authorization form needs to be filled in and submitted to the TPA within a certain time frame. The time frame is 2-4 days in advance for a planned hospitalization and within 24 hours of an emergency hospitalization. Up on hospitalization, the health card and an identity proof should be submitted to the hospital for facilitating the cashless benefit.
What is Pre-authorization? How do I intimate for cashless claim? What happens to cashless claim procedure for emergency hospitalization?
Pre-authorization means seeking approval or guarantee from the insurance company for payment of claims for the covered expenses. This approval might be sought by the policyholder or the hospital from the insurance company or from the company’s TPA. A pre-authorization form is required to be filled in and submitted for seeking such an approval. Intimation of claims can be done by informing and submitting the pre-filled Pre-authorization form to the insurance company or the TPA. In case of an emergency hospitalization, the insurer or the TPA should be informed immediately up on hospitalization and the Pre-authorization form should be submitted within 24 hours of hospitalization.
Can a request for authorization of a cashless claim be rejected /repudiated?
Rejection or repudiation of a request for authorization is possible in many scenarios. Firstly, if the treatment or hospitalization is for an ailment or a disease which is not covered under the plan, the request would be rejected. Secondly, if the amount of Sum Assured is exhausted from a previous claim, repudiation is inevitable. Lastly, if the policy is in a lapsed state, the authorization request would be rejected.
What are network hospitals? Is cashless facility available across all hospitals like AIIMS, etc.?
Hospitals which are in a contractual tie-up with insurance companies to render cashless treatments to their insured policyholders are called network hospitals. Cashless facility is available only in network hospitals which have a tie-up with the insurance company.
What is a reimbursement claim?
In case a policyholder gets admitted to a non-network hospital, cashless facility would not be available for the settlement of claims. In these cases, the policyholder would have to bear the medical expenses himself and then later get them reimbursed from the insurance company by submitting the required bills and documents. This type of claim is called a reimbursement claim.
What is the procedure for availing reimbursement claim?
For availing a reimbursement claim, the insurer or the concerned TPA should be informed of the= treatment and the hospital details. To raise a claim all necessary documents are to be submitted to the insurance company. Such documents include the claim form which should be duly filled and signed, Discharge Certificate from hospital, all documents which relate to the illness for which treatment was availed, all hospital bills, prescriptions and reports, certificate from surgeons, attending doctors and any medical practitioners whose services are availed, etc.
What is co-payment?
The co-payment clause is applicable in policies issued to older individuals. Under this clause, in case of any claim, the policyholder is supposed to pay a pre-determined proportion of the claim from his own pocket and the insurance company would pay the remainder. For instance, a co-pay of 10% means than in the event of a claim of Rs.1 lakh, Rs.10, 000 would have to be paid by the policyholder while the insurance company would pay the remaining Rs.90,000.
How to claim from two different insurance companies?
Claiming from two different companies might become necessary if the actual claim is in excess of the coverage of any one policy. In such a case, the original medical bills would have to be submitted to one insurance company which would settle the claim partly. Then, the copies of such medical bills would have to be attested by the hospital from which the treatment was taken and submitted to the other insurer along with the claim settlement summary from the first insurer. The second insurer would then reimburse the remainder of the claim. In case of a cashless treatment, two pre- authorization forms would have to be filled and submitted with both the insurers. Then the process is similar as described above.
Can any claim be rejected or refused?
Yes, your claims can be rejected or refused in some instances which include the following:
- The Sum Assured has been exhausted for the said policy year.
- The claim is made for an illness or a treatment which is specifically excluded from coverage.
- Claims are not made in the required time
- Documentation is incomplete
- The policy is in a lapsed state at the time of claim.
- If the claim made is fraudulent.
When will my claim be reimbursed?
Once the claim processing formality is completed and all the required documents have been submitted to the TPA or the insurer, the claim would be reimbursed.
What is No Claim Bonus?
A health plan runs for one year after which renewal is required. If during the year there is no claim under the plan, the year is called a claim-free year. For every claim-free year, the policyholder is entitled to receive a No Claim Bonus. This bonus can be in the form of an increase in the Sum Assured at the same level of premium or other discount offers. This bonus is cumulative in nature and accumulates every year for each claim-free year.
Will I lose my entire NCB when I claim?
No, the entire accumulated NCB is not lost on making a claim. The level of such NCB is usually reduced a little.
What is health insurance portability?
Health insurance portability means a change in the coverage provider while other terms and conditions of the policy remain the same. On renewals, policyholders have the choice to continue their coverage with the same insurer or switch to a similar plan of another insurer. This switching of insurers is called portability. In portability, the accumulated benefits of the previous policy can be continued with the new policy.
Will I have a waiting period if I port my health insurance policy?
Upon porting, the previous plans accumulated benefits continue. If you have already waited out the waiting period of your pre-existing illnesses in the last plan, you would not have any new waiting period. If a part of the waiting period is remaining, you would have to wait out only the remainder waiting period in the new policy. This continuation of the waiting period is possible if the Sum Assured of the old plan is continued. If you opt to increase the Sum Assured in the new plan, you would have to wait out the waiting period for the part of the Sum Assured which has been increased as it would be treated as a new policy.
What is a Top-Up Plan?
A top-up plan is a health plan which aims to increase the level of coverage at very low premium rates. These plans have a deductible limit. When claims are lower than the deductible limit, no claims are payable by these plans. However, claims above the deductible limit are payable by top-up plans. These plans can be taken along with existing health plans to increase the coverage level with very little increase in premium rates.
How does a top-up plan work?
Top-up plans have a threshold limit called the ‘deductible limit’. When a claim is made, the amount of claim is compared against the deductible limit. If the claim is lower than the deductible limit, the plan does not get activated. When the amount of claim crosses the deductible limit, the plan is triggered and the claim is paid.
Can I cancel my policy and if yes will I get my premium back?
After the policy is issued, insurance companies allow a cooling-off period of 15 days to the policyholder. During these 15 days if the policyholder wants, he can cancel the policy. Once the policy is cancelled, the premium paid is refunded after being adjusted for relevant taxes and other incidental expenses. Even after the completion of the cooling-off period, a policyholder can cancel his policy anytime during the policy year. Upon such cancellation, the premium would be refunded at the insurer’s short period rate which is as follows:
- If cancelled within 1 month 3/4th of the premium is refunded
- If cancelled within 3 months 1/2th of the premium is refunded
- If cancelled within 6 months 1/4th of the premium is refunded
- If cancelled after 6 months Nothing is refunded
What is free-look period?
Free-look period is the cooling-off period within which the policy can be cancelled and full premium can be availed after adjustment of statutory charges. A period of 15 days post policy issuance is allowed as the free-look period. So, if you are not satisfied with the policy, you can cancel the policy during this free-look period of 15 days and avail a refund of your premium from the insurance company.
Why should I buy travel insurance?
To obtain a visa for some countries, overseas travel insurance is compulsory. Even where it is not, it is prudent to obtain a travel insurance policy when you are travelling on business or holiday or for education, research etc as medical treatment costs in many countries are much higher than what they are in India and are unaffordable.
Can I extend the period of my travel insurance?
You must check with your insurer regarding this as it would depend on the policy. Read your policy document and understand what it provides. Most policies, especially overseas travel insurance policies have a provision for one or even two extensions.
Is there a minimum duration of period for purchase of travel insurance?
Generally there will be a minimum stipulated period. Normally pricing of the policy goes by the “trip band” i.e., the number of days of travel involved and there would be a minimum trip band.
Is a medical check -up required to purchase a travel insurance policy?
You must check up with the insurer and/or the agent or broker about medical tests required and reports that are required to be submitted along with the duly filled in proposal form. Check up about the validity period of such reports as well—normally reports within three to four weeks prior to departure are required.
Do I need prior approval of the insurance company before proceeding with medical treatment should the contingency arise?
Please read the policy thoroughly and understand whether there are such requirements. Prior approval would be required in most cases though there could be exceptions depending on the emergency involved. Get this aspect clarified at the time of purchasing the policy.
Who is a Third Party Administrator?
A Third Party Administrator is one who offers claims services on behalf of the insurer. In most cases, they offer cashless facility. You must confirm details from your insurer before you travel. Ensure that your policy document has all the contact details and other relevant information related to the services offered by the Third Party Administrator.
Can I get a refund under my policy if I cut short my travel?
In case your travel doesn’t take off and you show proof of the same, policies would normally provide for premium refund subject to deductions towards administrative costs. Where travel is cut short, policies may or may not allow refund subject to certain conditions. You must read your document and understand whether there is such a provision and if so, how it operates.
Is my visa status relevant to obtain overseas travel insurance?
In most cases it would be. Normally, such policies are meant for travellers who visit other countries on business or holiday or education or other purposes and not for those residing permanently abroad.
Is my visa status relevant to obtain overseas travel insurance?
In most cases it would be. Normally, such policies are meant for travellers who visit other countries on business or holiday or education or other purposes and not for those residing permanently abroad.
What should I look for before I decide to buy a policy?
You must check and see whether or not there is availability of guarantee of return, what the lock in period is, details of premium to be paid, what would be implications of premium default, what the revival conditions are what the policy terms are, what are the charges that would be deducted, would loan be available etc.
What is the importance of a proposal and the disclosures made therein?
The disclosures made in a proposal are the basis for underwriting a policy and therefore any wrong statements or disclosures can lead to denial of a claim.
What are special medical reports required to be submitted in Life insurance?
In case of certain proposals, depending upon the age of entry, age at maturity, sum assured, family history and personal history, special medical reports may be necessary for consideration of a risk. E.g. if the proposer is overweight, special reports like Electro Cardiogram, Glucose Tolerance test etc could be required, while for underweight proposers, X-ray of the chest and lungs with reports could be required.
What is meant by Paid-up Value in Conventional Life Insurance Policy?
After premiums are paid for a certain defined period or beyond and if subsequent premiums are not paid, the sum assured is reduced to a proportionate sum, which bears the same ratio to the full sum assured as the number of premiums actually paid bears to the total number originally stipulated in the policy. For example, if sum assured is 1 lakh and the total number of premiums is payable is 20 (20 years policy, mode of premium is assumed yearly) and default occurs after 10 yearly premiums are paid, the policy acquires the paid up value of 50,000/-. Paid up Value = No. of Premiums Paid / No. of Premiums Payable X S.A=10/20 X 100000 = 50000/-. This means that the policy is effective as before except that from the date the 11th premium was due, the sum assured is 50,000/- instead of original 1,00,000/-. To this sum assured the bonus already vested (accrued) before the policy lapsed, is also added. Example if the bonus accrued up to the date of lapse is 35,000/-, the total paid up value is 50000 + 35000 = 85000.
How is Surrender Value calculated in Conventional Life Insurance Policy?
Surrender Value is allowed as a percentage of this paid up value. Surrender value is calculated as per the surrender value factor, which depends on the premiums paid and elapsed duration.
How is the Loan on Policy calculated under Conventional Life Insurance Policies?
If the policy conditions permit grant of loan, loan is sanctioned as a percentage of the Surrender Value.
What are the requirements to be submitted in case of a Maturity Claim?
Usually the Insurance Company will send intimation attaching the discharge voucher to the policy holder at least 2 to 3 months in advance of the date of maturity of the policy intimating the claim amount payable. The policy bond and the discharge voucher duly signed and witnessed are to be returned to the insurance company immediately so that the insurance company will be able to make payment. If the policy is assigned in favour of any other person the claim amount will be paid only to the assignee who will give the discharge.
What is meant by settlement options?
Settlement option means the facility made available to the policy holder to receive the maturity proceeds in a defined manner (the terms and conditions are specified in advance at the inception of the contract).
What documents are generally required to be submitted in case of death of life assured while the policy is in force?
The basic documents that are generally required are death certificate, claim form and policy bond, Other documents such as medical attendant's certificate, hospital certificate, employer's certificate, police inquest report, post mortem report etc could be called for, as applicable. The claim requirements are usually disclosed in the policy bond.
What are Corporate Fixed Deposits ?
Corporate Fixed Deposits are deposits placed by investors with companies for a fixed term carrying a prescribed rate of interest.
How to choose a good Corporate deposit scheme ?
Avoid unrated Corporate Deposit Schemes. Avoid deposit schemes of little known manufacturing companies. For NBFCs, RBI has made it mandatory to have an ‘A’ rating to be eligible to accept public deposits. We would recommend that you go further and look at only AA or AAA schemes.
Choose the Corporate with a better reputation given similar ratings.
Once you decide on a Corporate, choose the schemes that have given a better return. Unless you need income regularly, you should prefer cumulative schemes to regular income options since the interest earned automatically gets reinvested at the same coupon rate, resulting in better yields. It also gives you a lump-sum amount at one go.
It is advisable to make shorter deposit of around 1 year to 2 years. It helps you to keep a watch on the Corporate’s rating and servicing and is easier to get the refund of the money in case of emergencies.
Please check on the servicing standards of the Corporate. You should not invest in companies that don’t pay attention to client services like sending interest warrants or the principal cheque on time.
We recommend that you Involve your Financial Planner / Investment Advisor for advice in all your transactions.
Check whether the Corporate accepts outstation cheques and makes payment through at par cheques, especially if you do not live in the same city where the Corporate is situated.
It is advisable to make shorter deposit of around 1 year to 2 years. It helps you to keep a watch on the Corporate’s rating and servicing and is easier to get the refund of the money in case of emergencies.
Please check on the servicing standards of the Corporate. You should not invest in companies that don’t pay attention to client services like sending interest warrants or the principal cheque on time.
We recommend that you Involve your Financial Planner / Investment Advisor for advice in all your transactions.
Check whether the Corporate accepts outstation cheques and makes payment through at par cheques, especially if you do not live in the same city where the Corporate is situated.
What type of companies accept deposits ?
Companies registered under the Companies Act 1956, such as: Manufacturing Companies,Non-Banking Finance Companies,Housing Finance Companies, Financial Institutions, Government Companies.
Upto what limits can a Corporate accept deposit ?
A Non-Banking Non-Finance Corporate(Manufacturing Corporate) can accept deposits subject to following limits-Upto 10% of the aggregate of paid-up share capital and free reserves if the deposits are from shareholders or guaranteed by the directors. Otherwise upto 25% of the aggregate of paid-up share capital and free reserves.
A NBFC can accept deposits upto following limits:
Equipment Leasing Corporate can accept four times of its net owned fund. Loan or Investment Corporate can accept deposit upto one and half time of its net owned funds.Companies where you should exercise caution before deciding to invest:
- Companies that offer excessively higher rates of interest
- Companies that are not paying regular dividends to the shareholders.
- Companies whose Balance Sheet shows losses.
- Companies that are below investment grade (A) or less rating.
How are Interest payments made ?
Interest is paid on Monthly/Quarterly/Half-Yearly/Yearly basis or on maturity, and is sent through Electronic Clearing System basis.
What is a Mutual Fund ?
A Mutual Fund is a trust that pools the savings of a number of investors who share a common financial goal. The money thus collected is then invested in capital market instruments such as shares, debentures and other securities. The income earned through these investments and the capital appreciation realised are shared by its unit holders in proportion to the number of units owned by them. Thus a Mutual Fund is the most suitable investment for the common man as it offers an opportunity to invest in a diversified, professionally managed basket of securities at a relatively low cost.
What are the Advantages of Investing in Mutual Funds ?
1. Professional Management - The basic advantage of funds is that, they are professional managed, by well qualified professional. Investors purchase funds because they do not have the time or the expertise to manage their own portfolio. A mutual fund is considered to be relatively less expensive way to make and monitor their investments.
2. Diversification - Purchasing units in a mutual fund instead of buying individual stocks or bonds, the investors risk is spread out and minimized up to certain extent. The idea behind diversification is to invest in a large number of assets so that a loss in any particular investment is minimized by gains in others.
3. Economies of Scale - Mutual fund buy and sell large amounts of securities at a time, thus help to reducing transaction costs, and help to bring down the average cost of the unit for their investors .
4. Liquidity - Just like an individual stock, mutual fund also allows investors to liquidate their holdings as and when they want.
5. Simplicity - Investments in mutual fund is considered to be easy, compare to other available instruments in the market, and the minimum investment is small. Most AMC also have automatic purchase plans whereby as little as Rs. 2000, where SIP start with just Rs.50 per month basis.
6. Regulated by SEBI and AMFI – please visit their websites for further information.
What is Net Asset Value (NAV) of a scheme?
The performance of a particular scheme of a mutual fund is denoted by Net Asset Value (NAV). Mutual funds invest the money collected from the investors in securities markets. In simple words, Net Asset Value is the market value of the securities held by the scheme. Since market value of securities changes every day, NAV of a scheme also varies on day to day basis.
Is PAN mandatory for investing in Mutual Funds?
No. As per SEBI guidelines an investor can invest upto Rs.50,000 per AMC without a Permanent Account Number in a year. The investor can also invest as an SIP provided the Rs.50,000 ceiling is maintained.
Can non-resident Indians (NRIs) invest in Mutual funds?
Yes, non-resident Indians can also invest in mutual funds. Necessary details in this respect are given in the offer documents of the schemes. Contact us for more information…..(put hyperlink on Contact Us).
What is a SIP ?
Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is an investment vehicle offered by Mutual Funds to investors, allowing them to invest small amounts periodically instead of lump sums. The frequency of investment is usually monthly.
Eg. A person wishes to invest Rs. 24000/- in a fund but due to other obligations, it is not possible for him to invest such an amount in a fund. He takes the SIP route and contributes to the fund Rs. 2000/- monthly for a year. At the end of the year, he’ll have invested Rs. 24,000/- in the fund. When the NAV is high, he will get the fewer units and when the NAV is low, he’ll get the more units. So, he’ll get the benefit of averaging through the SIP route.
The NAV in the first month was Rs. 10/-, he’ll get 200 units in the first month
The NAV in the second month was Rs. 9.50/-, he’ll get 210.52 units in second month
The NAV for the following month was Rs. 10, he’ll get 200 units in the next month
So, at the end of the year he may get more units as compared to the units he’ll get through single investment.
Eg. A person wishes to invest Rs. 24000/- in a fund but due to other obligations, it is not possible for him to invest such an amount in a fund. He takes the SIP route and contributes to the fund Rs. 2000/- monthly for a year. At the end of the year, he’ll have invested Rs. 24,000/- in the fund. When the NAV is high, he will get the fewer units and when the NAV is low, he’ll get the more units. So, he’ll get the benefit of averaging through the SIP route.
The NAV in the first month was Rs. 10/-, he’ll get 200 units in the first month
The NAV in the second month was Rs. 9.50/-, he’ll get 210.52 units in second month
The NAV for the following month was Rs. 10, he’ll get 200 units in the next month
So, at the end of the year he may get more units as compared to the units he’ll get through single investment.
What are the advantages of investing in a SIP ?
- Power of Compounding – Investing regularly in a SIP ensures that you keep investing irrespective of Market movements. Also, investing for a long time period helps you enjoy the compounding returns. Click here (Hyperlink to Visualize the Power of Compounding Section) to visualize the Power of Compouding.
- SIPs will ensure that you invest every month, thereby instilling discipline in your investment behaviour.
- SIPs are flexible – There is no fixed tenor for running SIP. Once the SIP tenor is fixed, it can be stopped in between or could be continued even after the tenor by placing a request. Also, full and partial withdrawal is possible during or after the SIP tenor. The SIP amount can be increased or decreased.
- Rupee cost averaging – Timing the market is a difficult task. Rupee cost averaging is an automatic market-timing mechanism that eliminates the need to time one`s investments. Here, one need not worry about where share prices or interest are headed as investment of a regular sum is done at regular intervals; with fewer units being bought in a declining market and more units in a rising market. Although SIP does not guarantee profit, it can go a long way in minimizing the effects of investing in volatile markets.
How can I invest in a SIP ?
You can start a SIP in the following steps :
- Decide on a SIP amount based on your objectives. You can use the Power of Compounding (Hyperlink to Visualize the Power of Compounding Section) tool to have an idea as to how much wealth can be accumulated over time at a given return.
- Narrow your choice of funds using the Blue Sky MF Select.
- We will help design your Portfolio using our In-house Research. Register with us in case you are not a Blue Sky customer. You can also use the Design my Portfolio (Hyperlink to the Design my Portfolio section) tool to have an illustrative understanding of the Asset Allocation based on your Risk Profile.
- You can either start the SIP Online using your Blue Sky Account, or you can do it offline. We will assist you for your convenience.
What are the different types of Mutual Fund schemes?
Equity Oriented Scheme
The aim of Equity funds is to provide capital appreciation over the medium to long- term. Such schemes normally invest a major part of their corpus in equities. Such funds have comparatively high risks. These schemes provide different options to the investors like dividend option, capital appreciation, etc. and the investors may choose an option depending on their preferences. Growth schemes are good for investors having a long-term outlook seeking appreciation over a period of time.
Income / Debt Oriented Scheme
The aim of income funds is to provide regular and steady income to investors. Such schemes generally invest in fixed income securities such as bonds, corporate debentures, Government securities and money market instruments. Such funds are less risky compared to equity schemes. These funds are not affected because of fluctuations in equity markets. However, opportunities of capital appreciation are also limited in such funds. The NAVs of such funds are affected because of change in interest rates in the country. If the interest rates fall, NAVs of such funds are likely to increase in the short run and vice versa.
Balanced Fund
The aim of balanced funds is to provide both growth and regular income as such schemes invest both in equities and fixed income securities in the proportion indicated in their offer documents. These are appropriate for investors looking for moderate growth. They generally invest 40-60% in equity and debt instruments. These funds are also affected because of fluctuations in share prices in the stock markets. However, NAVs of such funds are likely to be less volatile compared to pure equity funds.
Monthly Income Plans
Invests maximum of their total corpus in debt instruments while they take minimum exposure in equities. It gets benefit of both equity and debt market. These scheme ranks slightly high on the risk-return matrix when compared with other debt schemes.
Gilt Fund
These funds invest exclusively in government securities. Government securities have no default risk. NAVs of these schemes also fluctuate due to change in interest rates and other economic factors as is the case with income or debt oriented schemes.
Short Term Plans (STPs)
These Funds are meant for an investment horizon of three to six months. These funds primarily invest in short term papers like Certificate of Deposits (CDs) and Commercial Papers (CPs). Some portion of the corpus is also invested in corporate debentures.
Market or Liquid Fund
These funds are also income funds and their aim is to provide easy liquidity, preservation of capital and moderate income. These schemes invest exclusively in safer short-term instruments such as treasury bills, certificates of deposit, commercial paper and inter-bank call money, government securities, etc. Returns on these schemes fluctuate much less compared to other funds. These funds are appropriate for corporate and individual investors as a means to park their surplus funds for short periods.
Index Funds
Index Funds replicate the portfolio of a particular index such as the BSE Sensitive index, S&P NSE 50 index (Nifty), etc. These schemes invest in the securities in the same weightage comprising of an index. NAVs of such schemes would more or less rise or fall in accordance with the rise or fall in the index. There are also exchange traded index funds launched by the mutual funds which are traded on the stock exchanges.
The aim of Equity funds is to provide capital appreciation over the medium to long- term. Such schemes normally invest a major part of their corpus in equities. Such funds have comparatively high risks. These schemes provide different options to the investors like dividend option, capital appreciation, etc. and the investors may choose an option depending on their preferences. Growth schemes are good for investors having a long-term outlook seeking appreciation over a period of time.
Income / Debt Oriented Scheme
The aim of income funds is to provide regular and steady income to investors. Such schemes generally invest in fixed income securities such as bonds, corporate debentures, Government securities and money market instruments. Such funds are less risky compared to equity schemes. These funds are not affected because of fluctuations in equity markets. However, opportunities of capital appreciation are also limited in such funds. The NAVs of such funds are affected because of change in interest rates in the country. If the interest rates fall, NAVs of such funds are likely to increase in the short run and vice versa.
Balanced Fund
The aim of balanced funds is to provide both growth and regular income as such schemes invest both in equities and fixed income securities in the proportion indicated in their offer documents. These are appropriate for investors looking for moderate growth. They generally invest 40-60% in equity and debt instruments. These funds are also affected because of fluctuations in share prices in the stock markets. However, NAVs of such funds are likely to be less volatile compared to pure equity funds.
Monthly Income Plans
Invests maximum of their total corpus in debt instruments while they take minimum exposure in equities. It gets benefit of both equity and debt market. These scheme ranks slightly high on the risk-return matrix when compared with other debt schemes.
Gilt Fund
These funds invest exclusively in government securities. Government securities have no default risk. NAVs of these schemes also fluctuate due to change in interest rates and other economic factors as is the case with income or debt oriented schemes.
Short Term Plans (STPs)
These Funds are meant for an investment horizon of three to six months. These funds primarily invest in short term papers like Certificate of Deposits (CDs) and Commercial Papers (CPs). Some portion of the corpus is also invested in corporate debentures.
Market or Liquid Fund
These funds are also income funds and their aim is to provide easy liquidity, preservation of capital and moderate income. These schemes invest exclusively in safer short-term instruments such as treasury bills, certificates of deposit, commercial paper and inter-bank call money, government securities, etc. Returns on these schemes fluctuate much less compared to other funds. These funds are appropriate for corporate and individual investors as a means to park their surplus funds for short periods.
Index Funds
Index Funds replicate the portfolio of a particular index such as the BSE Sensitive index, S&P NSE 50 index (Nifty), etc. These schemes invest in the securities in the same weightage comprising of an index. NAVs of such schemes would more or less rise or fall in accordance with the rise or fall in the index. There are also exchange traded index funds launched by the mutual funds which are traded on the stock exchanges.
What are Tax Saving Schemes?
These schemes offer tax rebates to the investors under specific provisions of the Income Tax Act, 1961 as the Government offers tax incentives for investment in specified avenues. e.g. Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS). Pension schemes launched by the mutual funds also offer tax benefits. These schemes are growth oriented and invest pre-dominantly in equities. Their growth opportunities and risks associated are like any equity-oriented scheme.
Can an investor appoint a nominee for his investment in units of a Mutual Fund?
Yes. The nomination can be made by individuals applying for / holding units on their own behalf singly or jointly. Non-individuals including society, trust, body corporate, partnership firm, Karta of Hindu Undivided Family, holder of Power of Attorney cannot nominate.
I am going to retire soon? Can I invest and get a monthly interest as income?
Out-Living your resources possesses a very high risk during your retirement years, choosing you’re a correct asset allocation is critical for a successful retired life. Their many products one can choose from to start receiving immediate income (annuity). Some of the products that can offer you immediate annuity include bonds, FDs, Post office MIS, tax free bonds, annuity plans from life insurance companies. Factors such as product specific risks, lock-in-period, taxation and liquidity should be considered along with your asset allocation strategy before finalizing a product or a basket of products.
Why do disclaimers say mutual funds are subject to market risks? What have those got to do with trading, I thought they are fixed interest.
Why do disclaimers say mutual funds are subject to market risks? What have those got to do with trading, I thought they are fixed interest.
Why can’t I just invest in a bank and get interest, why take a risk like this?
Not taking the risk is the biggest risk one can take when it comes to investment. Just consider this hypothetical example: You have 100 Rupees today from which you can buy 10 bottles of water. You decide to invest this Rs. 100 in to saving bank account which gives 4% interest. Now after a year when you withdraw Rs. 104/-( Principle 100+ Rs. 4.00 interest) you will not be able to buy 10 water bottle as by now the price of the bottle has increased to Rs.11 per bottle and cost of 10 bottle will be Rs 110/-. Instead of not taking risks we can take calculated risks by investing a part of our hard earns money into equity which can take care of the monster called “inflation”. And also the investment in bank fixed deposits is secured up to Rs. 1 lakh, only protected with insurance over and above that amount it is also not secured.
We witness many examples in our life where people struggle to keep their standard of living intact or settle down with less luxury because they don’t plan their finances in their early days. It takes only Rs.6000 per month to invest and have corpus of Rs. 1crore at the age of 50 for a 25 year young earner (assuming: ROI @ 12%).
We witness many examples in our life where people struggle to keep their standard of living intact or settle down with less luxury because they don’t plan their finances in their early days. It takes only Rs.6000 per month to invest and have corpus of Rs. 1crore at the age of 50 for a 25 year young earner (assuming: ROI @ 12%).
How soon can I see profits if I start investing today?
Investing is a long-term process and one should not expect immediate returns for the product. The typical investment horizon for an investment in equity and equity linked products ranges from a minimum of 3 to 5 years. There are many reasons why you should stay invested for a longer time such as erratic market movements during shorter periods which can lead to equity markets giving negative returns, long business cycles, government and regulatory changes, global and local events, micro and macro events and to benefit of power of compounding etc. If you have an investment horizon below this then you should park your money in to safer asset classes such as debt schemes from mutual funds and Bank FDs
Who are eligible to open online trading account?
Any individual, HUF (Hindu Undivided Family), proprietary firm, partnership firm or a corporate can open online trading account with Aditya Birla Money.
How to open an Online Account ?
It is very simple! Just choose from below mentioned options to contact us :
- Register yourself with us (Link to : Register Page)
- Email us at contact@blueskygroup.in
- Call us at +91 33 4064-8131/4001-9504
How many exchanges can I trade on ?
You can trade on NSE, BSE, MCX, NCDEX and MCX-SX on single platform.
What instruments are traded in the stock markets?
There are various types of instruments traded in the stock market. They include shares, IPOs, futures and options.
What are some of the orders i can place?
You can place different kinds of orders such as market orders, limit orders, stop loss orders, good-till-cancelled orders, after-market orders (AMOs), etc
What is Market Order?
A market order is an order to buy or sell a stock at the current market price. It signals your broker to execute the order at the best price currently available. However, as market prices keep changing, a market order cannot guarantee a specific price.
What is Limit Order?
To avoid buying or selling a stock at a price higher or lower than you wanted, you need to place a limit order rather than a market order. A limit order is an order to buy or sell a security at a specific price. You could use a limit order when you want to set the price of the stock. In other words, you want to sell/buy particular scrip at a price other than the current market price. However, although a limit order guarantees a price, it cannot guarantee execution of the trade. This is because the stock might not reach the desired price on that particular trading day owing to market-related factors.
What is Stop Loss Order?
A stop loss order is a normal order placed with a broker to sell a security when it reaches a certain predetermined price called the trigger price. Sometimes the market movements defy your expectations. Such market reversals often result in loss-bearing transactions. The stop loss trigger price is your defense mechanism – an amount at which you will be able to sustain yourself against such unanticipated market movements. For example, if you bought a stock at Rs. 10, you place a stop loss order with your broker to sell it, if it reaches Rs. 8. This helps you prevent further loss, in the eventuality that the price of the stock might dip even further. Thus, it helps limit your loss or protect unrealized profits, whichever the case.
What happens in case my shares are short sold?
At any point of time when the shares are short sold and the same are not delivered to the exchange, the shares go in for auction. Here, the shares are purchased on behalf of the client in the auction market and delivered to the actual buyer.
How can you qualify the market as bull or bear?
Bull and bear markets signify relatively long-term movements of significant proportion. Hence, these runs can be gauged only when the market has been moving in its current direction (by about 20% of its value) for a sustained period. One does not consider small, short-term movements that last for a few days, as they may only indicate corrections or short-lived movements.
What is bottoming out?
Stock prices move in trends – an upward and a lower trend. During periods of bear markets, prices keep falling. However, there will come a time when the market starts to look cheap. This is when it starts to rise again as people start buying slowly. This phenomenon when the market free-fall ends and the rise begins is called bottoming out.
Similarly, on the higher end, there will come a point when too much buying has made the stock costly. Traders then start selling in droves to book profits. So, the price does not rise beyond this level. This is called 'peaking'.

Similarly, on the higher end, there will come a point when too much buying has made the stock costly. Traders then start selling in droves to book profits. So, the price does not rise beyond this level. This is called 'peaking'.

What are the various types of the risks once I start trading?
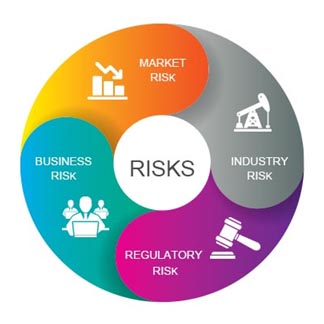
This is the risk of investing in the stock market in general. It refers to a chance that a security’s value might decline. Although a particular company may be doing poorly, the value of its stock can go up because the stock market value is collectively going up. Conversely, your company may be doing very well, but the value of the stock might drop because of negative factors like inflation, rising interest rates, political instability etc that are effecting the whole market. All stocks are affected by market risk.
Industry Risk
This is a risk that affects all companies in a particular industry. This is because the companies in an industry may work in a similar fashion. This exposes them to certain kinds of risk unique to the industry.
Regulatory Risk
Virtually every company is subject to some sort of regulation. It refers to the risk that the government will pass new laws or implement new regulations that will dramatically affect a business.
Business Risk
These are the risks unique to an individual company. It refers to the uncertainty regarding the organization’s ability to conduct its business. Products, strategies, management, labor force, market share, etc. are among the key factors investors consider in evaluating the value of a specific company.
